Advertising in AI Results
In mid-January 2026, OpenAI announced it will start testing ads in ChatGPT, placing clearly-labelled ads at the bottom of its responses. At the same time, Google is already injecting ads into its AI-driven search results. In Australia and New Zealand, Google has begun rolling out these AI Overview ads into search results.
For Kiwi marketers, this is a big deal. Ads in AI-powered results open up entirely new advertising spaces – but they also come with new rules and challenges. In this article, we’ll explain what “advertising in AI results” means, how ChatGPT and Google are implementing ads, and what this trend implies for New Zealand advertisers. We’ll cover the opportunities (new ways to reach customers) and the challenges (maintaining trust and adapting campaigns). By the end, you’ll know how to prepare your marketing strategy for the AI-advertising era.
What Are AI Search Results and Why Do They Matter?
AI search results are changing how people find information online. Instead of getting a list of blue links, you now get direct answers generated by artificial intelligence.
Google's AI Overviews appear at the top of many search results, synthesising information from multiple sources into one comprehensive response. ChatGPT's search function works differently—it provides conversational answers and can follow up with related questions. Both platforms are now introducing ads into these AI-generated responses.
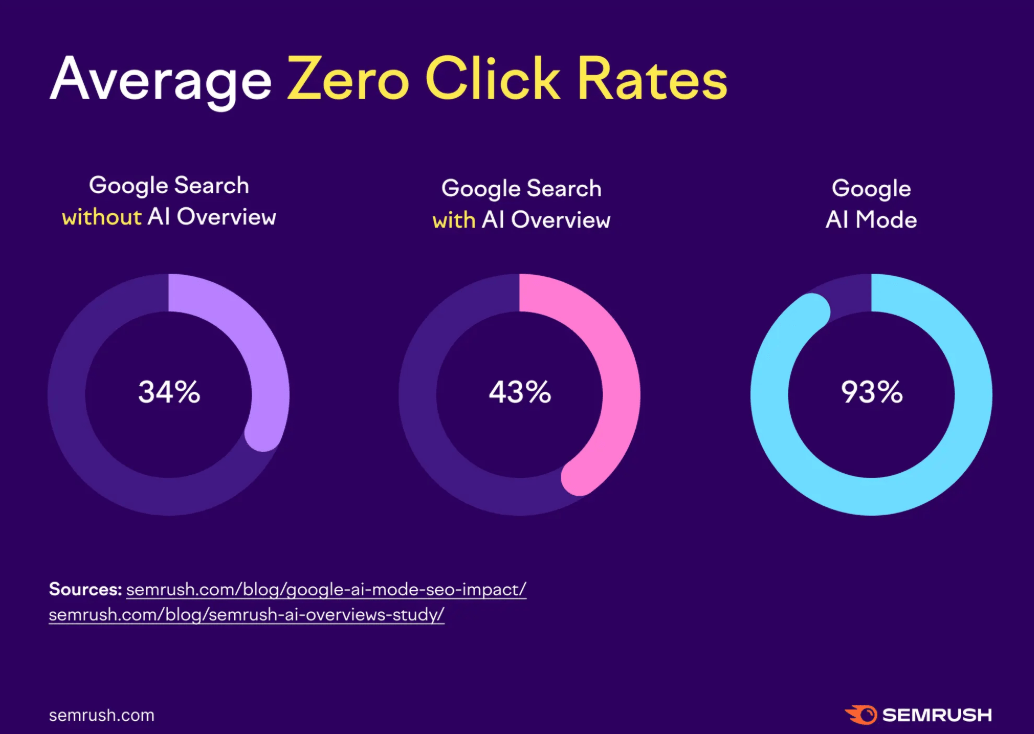
For New Zealand marketers, this matters because AI results are becoming the first thing people see when they search. Data from Semrush shows AI Overviews appeared in nearly 25% of queries during peak periods in 2025. That's a massive chunk of search traffic getting answers before they even click through to traditional results.
The shift is already impacting click-through rates. Research from Profound found organic CTR dropped 61% for queries with AI Overviews, while paid CTR fell 68%.
And SEMRUSH data shows exactly what happens: more and more searchers don’t need to click, they’re already finding out what they need to know, right there on the search results or AI query pages.
Your customers are getting their answers directly from AI—and if your brand isn't mentioned in those answers, you're invisible.
These AI-generated answers have become a new kind of search result. They often satisfy the user’s query without needing to click through to a website – what some call the “no-click” or “zero-click” phenomenon. As one NZ digital agency explains: “AI Overviews... appear right at the top of the page and search results” for long, specific queries. In short, AI results are quick answers from an AI, shown above the usual ads and links.
ChatGPT Ads: A New Channel for NZ Advertisers
ChatGPT is gearing up to be a new ad platform. In January 2026, OpenAI confirmed it will start testing ads in ChatGPT in the US first. These ads will show up at the bottom of ChatGPT’s answers. OpenAI emphasizes they will be clearly labeled and contextual to the conversation. For example, if you ask ChatGPT about buying a laptop, you might see an ad from a laptop maker at the end.
Key points about ChatGPT ads:
- Where and When: Ads will appear only in ChatGPT’s free tier and the new low-cost “Go” plan. Users who pay for higher tiers (Plus, Pro, Business) will not see ads. Initially, ads will be tested in the US, but a worldwide rollout is expected in 2026. (A paid NZ ChatGPT plan should let Kiwi users avoid ads, just like Plus or Enterprise will in the US.)
- How They Work: OpenAI says ads will appear at the bottom of the answer when there’s a relevant offer to promote. They will not influence the answer itself; ChatGPT’s replies will remain focused on being helpful. OpenAI promises “answers are optimized based on what’s most helpful to you” and that ads are always separate.
- Privacy and Safety: According to OpenAI, user conversations in ChatGPT won’t be shared with advertisers. They will also block ads related to sensitive topics like health or politics, and users under 18 won’t see ads. This is meant to maintain user trust.
- Opting Out: OpenAI plans to let you opt out of ads by paying for a higher subscription. The $8/month “Go” plan will still have ads, but the $20/month Plus plan (and above) will remain ad-free.
The revenue potential is huge. Internal OpenAI documents project $1 billion in revenue from free user monetisation starting in 2026, growing to nearly $25 billion by 2029. With 800 million weekly active users and only about 5% paying for subscriptions, advertising is the only realistic way to fund the platform's massive infrastructure costs.
For Kiwi marketers, this creates an opportunity. ChatGPT usage is growing globally, and New Zealand consumers are early adopters of new technology. When ChatGPT ads launch locally—likely within 3-6 months of the US rollout—early advertisers could benefit from lower costs and less competition.
Implications of ChatGPT Ads
For NZ advertisers, ChatGPT ads are a brand-new opportunity – but also something to approach carefully:
- A Huge Audience: ChatGPT claims hundreds of millions of users globally. If even a fraction of Kiwi internet users are on ChatGPT, it’s a big audience. Advertisers might get to reach people precisely when they’re asking questions, not just when they’re searching on Google.
- Untapped Keywords: Early analysis suggests that very few brands are targeting ads in AI chat yet. Chat queries are often long and broad, not the precise keywords used in search ads. For example, nobody usually bids on “how to clean a green pool” – it’s not a typical shopping query. But an AI ad could show up there naturally. NZ marketers can get in early on these “no one right answer” queries.
- Trust Matters: Some experts warn this new ad model could erode trust. As security experts Schneier and Sanders note, AI platforms adding ads is a bit like social media: it risks “covert manipulation” and tracking users. E-marketer analyst Jeremy Goldman cautions that if ChatGPT ads feel clumsy or irrelevant, users might switch to alternatives (Google’s Gemini, Claude, etc.). So ads must be relevant and unobtrusive.
- Cost and Competition: No one yet knows what pricing will be. Google dominates search ads, but ChatGPT might offer lower competition initially. NZ brands that experiment and learn early could have an edge – but they’ll need to figure out what works in a conversation-driven format.
Google’s Move: Ads in AI-Powered Search
While ChatGPT is just starting with ads, Google's been running them in AI Overviews since mid-2025. The expansion to desktop and additional markets throughout 2025 means more New Zealand searches now include AI-generated answers with integrated advertising.
Google's approach differs from ChatGPT. Ads appear both alongside and within AI Overview responses, blending sponsored content with organic information. The integration is subtle—ads look similar to traditional search ads but are contextually matched to the AI-generated answer.
AI Mode—Google's conversational search interface—also includes ads. This feature handles multi-step queries where users ask follow-up questions, similar to ChatGPT. Ads may appear below and integrated into AI Mode responses.
The data tells an interesting story. Despite initial concerns, click-through rates for keywords with AI Overviews have actually risen since January 2025. Google's testing suggests AI Overviews don't automatically reduce clicks—they might even encourage them for the right queries.
For New Zealand marketers, Google's AI advertising is already accessible through existing Google Ads accounts. The challenge is making your ads relevant enough to appear in AI contexts, which requires understanding how AI selects content.
Emerging competitors
Perplexity AI, Claude, Gemini, and other AI platforms are developing their own monetisation strategies. Perplexity has already tested sponsored questions and may introduce advertising before ChatGPT fully rolls out.
For Kiwi marketers, this fragmentation means you can't put all your eggs in one basket. A multi-platform approach will be necessary, just as you currently advertise across Google, Facebook, and other channels rather than relying on a single platform.
How AI Advertising Actually Works: What Marketers Need to Know
Understanding how AI selects which brands to mention or advertise is the first step to succeeding in this new channel.
Relevance matching: AI systems don't just look for keywords—they understand intent. If someone asks "best running shoes for flat feet," the AI breaks this into concepts like foot problems, athletic footwear, and product recommendations. Your content needs to address these concepts comprehensively, not just include the exact phrase.
Quality signals: Google and ChatGPT prioritise authoritative, trustworthy sources. This means established brands with strong online presence have an advantage, but smaller businesses can compete by demonstrating clear expertise in their niche.
Brand mentions: Research from Ahrefs found that brands mentioned frequently across the web get featured more often in AI results. If people are talking about your business on news sites, forums, social media, and other platforms, AI systems recognise you as a credible option.
Structured data: Machine-readable content like schema markup helps AI understand your business. Product specifications, reviews, business hours, and FAQ schema all make it easier for AI to extract and present your information accurately.
Content freshness: AI systems favour current information for topics that evolve. A blog post from June 2026 discussing AI advertising will outrank an authoritative but outdated article from 2022 on the same topic.
The practical implication: you can't just buy your way into AI results with ads alone. Your organic presence, content quality, and brand authority all influence whether AI systems consider you worth mentioning or advertising.
Opportunity and Impact for NZ Advertisers
This Google move means New Zealand advertisers should update how they think about search marketing. Consider:
- New Search Inventory: AI Overviews are showing up on lots of queries that were once only “informational.” These weren’t great for ads before, but now Google finds the commercial angle and lets relevant ads appear. In other words, queries that were too broad or top-of-funnel are suddenly monetizable. This uncovers “previously untapped moments of intent”.
- Converged SEO/PPC: Google’s AI reads your website content to understand intent. In practice, your paid search results may increasingly rely on the quality of your content. The Conversion Marketing blog predicts a “great convergence” of SEO and PPC, since Google’s AI will use your content to determine ad relevance.
- First-mover advantage: Early advertisers on new platforms typically benefit from lower costs and less competition. When ChatGPT ads launch in New Zealand, brands that test immediately will gather data and optimise while competitors are still figuring out whether to participate.
- Analytics are Changing: One challenge is tracking. Right now Google doesn’t separate out “AI Overview ad” impressions in reporting. You’ll have to infer performance from aggregate Search reports. Expect this to improve over time, but be aware that early metrics may be a bit murky.
Overall, Google’s AI-overview ads are an evolution of paid search in NZ. They give advertisers extra real estate on search pages, but they also raise the bar: ads must be directly relevant and helpful.
Challenges and Risks to Consider
AI advertising isn't all upside. Kiwi marketers need to understand the potential pitfalls before committing budget.
Trust and bias concerns: If users perceive AI as serving advertisers rather than their interests, the whole system loses credibility. OpenAI CEO Sam Altman himself called combining ads with AI "uniquely unsettling" in previous interviews, even though the company's now doing exactly that.
Limited control: You can't target AI placements directly yet. Your ads need to be relevant to both the query and the AI-generated answer, which introduces variables you can't fully control through traditional campaign settings.
Measurement complexity: Standard metrics like impressions and clicks might not tell the full story with AI advertising. How do you measure the value of being mentioned in an AI response versus appearing in a traditional ad slot?
Higher competition costs: While early adopters might enjoy lower costs, AI advertising will eventually attract major brands with large budgets. Google's AI advertising infrastructure is already well-developed, and competition is heating up.
Platform dependency: Building your strategy around ChatGPT or Google AI means relying on platforms that could change policies, pricing, or features at any time. Diversification across channels remains important.
Content quality requirements: AI advertising demands higher-quality content and stronger brand authority than traditional ads. You can't just buy your way in—you need to deserve the visibility.
One Major Challenge
Perhaps the biggest single challenge for marketers is the informational nature of many AI queries. Unlike traditional Google ads, where you can be highly prescriptive and focus on transactional, commercial keywords (“buy”, “price”, “near me”), AI search is much more conversational. People ask messy, human questions: “What’s the best way to reduce damp in an old villa?” or “How do I choose an accountant for my small business?” Those queries often sit well above the point of purchase. That’s great for helping users, but it creates real tension for advertisers: your ad can show up earlier in the journey, yet the intent can be vague, curious, or purely research-driven.
The knock-on effect is that you may end up handing more control of your budget to algorithms. To get visibility in AI Overviews and other AI-driven placements, you’re often pushed towards broader targeting, automated bidding, and campaign types that “figure it out” on your behalf. That can work brilliantly when the system correctly spots buying intent hiding inside an informational query. But it can also burn spend if the algorithm decides your ad belongs next to a topic that’s too broad, too early-stage, or simply not a fit for your offer. The practical response is not to avoid automation, but to put guardrails around it: tighter conversion definitions, smarter negative keyword and placement exclusions where available, clear audience signals, and ruthless landing-page alignment (so you only pay to show up when your offer truly helps the question being asked). In this new environment, your job shifts from micromanaging keywords to managing risk—and making sure the AI’s “best guess” doesn’t become your most expensive habit.
Privacy and Data Considerations
AI advertising raises privacy questions that Kiwi marketers need to address proactively.
OpenAI promises they won't sell user data to advertisers and that conversations remain private. Users can disable personalisation based on their chats. Google makes similar privacy commitments around AI Overview data.
But here's the reality: effective advertising requires data. The tension between privacy protection and ad effectiveness will shape how AI advertising develops.
What this means for marketers:
Be transparent about data usage in your advertising. New Zealand consumers value privacy, and brands seen as exploiting personal data face backlash.
Respect opt-out preferences. Users who disable ad personalisation should see less targeted ads, not just different ads.
Focus on contextual relevance rather than personal data. AI advertising enables targeting based on conversation context without requiring invasive personal data collection.
Comply with New Zealand privacy laws and international standards like GDPR. AI advertising must follow the same privacy regulations as other digital advertising.
Trust is Non-Negotiable
The trust factor matters more in AI advertising than traditional channels. People have intimate conversations with AI assistants—about health problems, financial struggles, relationship issues. Using that information for advertising crosses lines that traditional search advertising doesn't approach.
Brands that prioritise user trust over short-term advertising gains will build stronger long-term positions in AI advertising channels.
Opportunities for NZ Marketers
With these changes, Kiwi advertisers have some new opportunities:
- Expanded Reach: You can target searchers who are asking broader questions. For example, a local travel company could pop up in an AI answer about “best scenic drives in NZ,” even if the user didn’t search “book scenic drive.” Google’s AI infers intent and matches ads on its own.
- Less Competition (for now): Because AI chat ads are brand-new, fewer advertisers are bidding directly on ChatGPT or AI-overview keywords. Early adopters may get impressions and learnings with less competition than on Google Search.
- Better Audience Insights: Since AI chat platforms are conversational, you could frame ads more like helpful suggestions than overt selling. You might use questions in your ad copy (“Wondering which laptop suits you?”) or even set up simple chat-based campaigns in the future, as some predict.
- Performance Max and AI Tools: Google’s Performance Max campaigns, which automatically use multiple channels and AI to optimize for conversions, are particularly suited for this new landscape. If you adopt PMax now, you’re already preparing for AI-driven targeting. Similarly, exploring dynamic search ads and Smart Bidding can align your Google campaigns with AI’s context-based matching.
- AEO (Answer Engine Optimization): Just as you optimize for SEO, think about AEO – making sure your content can be referenced by AI answers. For local NZ businesses, adding structured data, keeping FAQs updated, and writing clear “how-to” content can help your site be cited by AI and improve your visibility, whether or not ads show up.
Action Plan for Kiwi Advertisers
You don't need to wait for ChatGPT ads to launch locally before taking action. Here's what Kiwi marketers should do now to prepare.
Build your content foundation: Create comprehensive, original content that addresses your audience's questions in depth. Think beyond blog posts—develop guides, case studies, video content, and resources that demonstrate real expertise.
Optimise for natural language: Write the way people actually talk and ask questions. Include FAQ sections, conversational headings, and direct answers to common queries. This helps both AI systems and human readers.
Strengthen your brand presence: Get mentioned on quality websites, earn media coverage, participate in industry discussions, and build genuine authority in your niche. AI systems notice when multiple credible sources reference your brand.
Implement structured data: Add schema markup to your website for products, services, FAQs, reviews, and business information. Make it easy for AI to understand and extract your content accurately.
Monitor AI results now: Start tracking how your brand appears (or doesn't appear) in Google AI Overviews and ChatGPT responses. Understanding your current visibility helps you measure improvement.
Test AI Max campaigns: If you're already using Google Ads, experiment with AI Max for Search campaigns. These features preview how AI-driven advertising will work and help you learn before ChatGPT ads arrive.
Stay informed on local rollouts: Watch for announcements about ChatGPT advertising expanding to New Zealand. OpenAI will likely announce before launch, giving you time to prepare campaigns.
Budget for experimentation: Set aside 5-10% of your paid advertising budget for initial AI advertising tests. This is small enough that poor performance won't hurt, but large enough to gather meaningful data.
The brands that succeed in AI advertising will be those that start building foundations now rather than waiting for formal platform launches.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Learning from early mistakes saves time and money. Here are pitfalls Kiwi marketers should avoid:
Waiting too long: "Let's see how it goes first" means watching competitors capture market share while you're stuck playing catch-up with higher costs and more competition.
Treating AI ads like traditional search ads: The targeting, creative requirements, and success metrics differ. Applying traditional search advertising logic directly won't work.
Ignoring organic presence: You can't just buy your way into AI results. Poor organic presence limits your AI advertising effectiveness.
Over-automation: Giving AI advertising platforms complete control without monitoring performance or setting appropriate guardrails leads to wasted spend.
Neglecting brand building: AI systems favour recognised brands. If you're unknown online, AI advertising alone won't solve that problem.
Poor content quality: Thin, generic content won't get selected by AI systems regardless of advertising spend. Quality threshold is higher than traditional advertising.
Single-platform focus: Putting all resources into ChatGPT or Google AI creates dependency risk. Diversify across platforms.
Skipping measurement setup: Start tracking baseline metrics now so you can measure impact when AI advertising launches.
The biggest mistake? Assuming AI advertising is just another trend you can ignore. This is a fundamental shift in how people find information and make decisions online.
What Makes Content "AI-Friendly"?
Getting your content selected by AI systems—whether for organic mentions or ad placement—requires understanding how these platforms evaluate quality.
Answer intent directly: When someone asks a question, answer it immediately and clearly. If a section is titled "What is conversion rate optimisation?" start with a concise definition, then elaborate. This makes it easy for AI to extract and quote your content.
Use comprehensive coverage: Don't just scratch the surface. If you're writing about email marketing for e-commerce, cover strategy, tools, metrics, best practices, common mistakes, and examples. AI favours content that satisfies user intent completely.
Include specific data: Statistics, research findings, and concrete numbers make your content more citable. "Email marketing generates an average ROI of 42:1" is more valuable to AI systems than "email marketing is cost-effective."
Demonstrate expertise: Include author credentials, cite authoritative sources, and showcase first-hand experience. AI systems check author qualifications and source credibility before citing content.
Write with clarity: Simple, direct language works better than complex jargon. Aim for high school reading level—this benefits both AI parsing and human readers.
Format for scannability: Use clear headings, short paragraphs, bullet points, and logical structure. Make it easy for AI (and humans) to quickly find specific information.
Keep content current: Update key pages regularly with fresh data, new examples, and current trends. AI systems favour recent information for topics that evolve.
The New Zealand context matters here too. Content addressing local business challenges, referencing Kiwi market conditions, and using region-specific examples will resonate more with AI systems serving New Zealand users.
AI Advertising Formats: What to Expect
Based on current implementations and industry analysis, here's what AI advertising formats will likely look like in 2026.
Sponsored responses: Ads appearing as clearly labelled content within or below AI-generated answers. ChatGPT's current implementation puts these at the bottom of responses with "sponsored" tags.
Contextual product recommendations: For shopping-related queries, expect integrated product suggestions with direct purchase options. OpenAI's partnership with retailers like Walmart and Etsy enables instant checkout within ChatGPT.
Sponsored citations: Your brand mentioned within AI responses as a suggested solution, with payment required for premium placement. This blends organic-looking mentions with paid promotion.
Visual ads: As AI platforms become more visual, expect image and video ads integrated into responses. Google's Asset Studio already helps advertisers create AI-generated visual content.
Conversational ads: Interactive ads where users can ask follow-up questions about products or services directly within the AI conversation. This takes engagement beyond traditional static ads.
Sidebar placements: Similar to traditional search ads, sponsored content appearing alongside AI responses rather than within them.
The key difference from traditional advertising: AI ads need to be genuinely relevant to the conversation context. Forced or irrelevant ads will likely be filtered out by AI systems or ignored by users who've come to expect helpful, contextual responses.
Measuring Success in AI Advertising
Traditional advertising metrics won't fully capture the value of AI advertising. You'll need to track additional signals to understand performance.
Citation frequency: How often does your brand get mentioned in AI responses, both organic and paid? Being cited first carries more weight than appearing fifth in a list.
Share of voice: What percentage of relevant AI responses include your brand compared to competitors? This metric matters more in AI than traditional advertising.
Assisted conversions: Someone might see your brand mentioned in ChatGPT, then search for you directly on Google hours later. Attribution becomes more complex when AI introduces customers to your brand.
Engagement depth: In conversational AI platforms, did users ask follow-up questions about your product? Did they click through to learn more? Engagement signals matter beyond simple clicks.
Brand lift: Survey-based metrics tracking whether AI exposure increased brand awareness, consideration, or preference among your target audience.
Quality of traffic: Leads from AI advertising might be fewer but more qualified, having already been pre-qualified by the AI conversation context.
For New Zealand marketers, establishing baseline measurements now—before AI advertising becomes mainstream—helps you quantify the impact when you do start advertising in these channels.
Looking Ahead: What Happens After 2026?
AI advertising this year is just the beginning. Here's what the next few years likely hold:
Platform consolidation: Some AI advertising platforms will succeed while others fade. The winners will likely be those offering the best combination of reach, relevance, and ROI.
Increased sophistication: Targeting capabilities, ad formats, and measurement tools will improve rapidly as platforms learn what works.
Higher costs: As more advertisers join and competition intensifies, advertising costs will rise. Early advantage goes to brands who establish presence before this happens.
Regulation: Governments will develop policies around AI advertising, particularly concerning privacy, transparency, and consumer protection. New Zealand may follow international regulatory frameworks.
New formats: We haven't seen the final form of AI advertising yet. Expect interactive experiences, voice-based ads, and formats we can't currently imagine.
Integration with other channels: AI advertising won't exist in isolation. Successful campaigns will integrate AI advertising with search, social, email, and other channels in sophisticated multi-touch strategies.
For New Zealand marketers, staying ahead means continuous learning and adaptation. The AI advertising landscape of 2029 will look very different from 2026, and brands that keep evolving will maintain competitive advantages.
Want to get upskilled in the use of AI for Advertising and Marketing?
At Netmarketing Courses we offer a range of AI courses, specifically designed to help marketers become effective AI practitioners (through our AI for Marketers course) and then grow to become AI marketing experts (through our Advanced AI for Marketers course).

Check out the details of our AI for Marketers online training course here.
Check out the details of our Advanced AI for Marketers online training course here.
We also offer specialist courses designed to help you use AI effectively for Retail Marketing, Tourism Marketing and Small Business Marketing.
FAQ
Q: When will ChatGPT start showing ads in New Zealand?
A: OpenAI hasn't announced specific launch dates for markets outside the US, but international rollouts typically follow within 3-6 months of US launches. Given ChatGPT ads started testing in the US in January 2026, we could see New Zealand availability by mid-2026. Watch OpenAI's official blog and advertising platform announcements for confirmation. Early indications suggest they'll expand to English-speaking markets like New Zealand, Australia, and the UK before other regions.
Q: How do Google’s AI overview ads work?
A: Google now inserts ads into its AI-generated summary boxes (AI Overviews) on search results. In New Zealand, advertisers can appear above, below or even inside these AI answers. Existing Search or Shopping campaigns can show ads around the AI response, but to appear within the AI summary itself you need broad-match keywords or Performance Max campaigns. Google’s system matches your ad to both the user’s query and the content of the AI overview. The result: ads on queries where people are learning or comparing, not just buying.
Q: Will ChatGPT ads use my personal data or target me specifically?
A: According to OpenAI, no personal conversation data is shared with advertisers. ChatGPT ads will be contextual – based on the content of your current chat prompts – not profile-based. OpenAI also says ads won’t appear for users under 18 or on certain topics like health or politics. In short, the ads are meant to be relevant suggestions, not creepy stalker-ads.
Q: What benefits do NZ advertisers get from ads in AI search results?
A: The main benefit is new reach. AI results capture searches that old-style ads didn’t. For example, if someone asks an AI a how-to question, your ad can still show up if it’s relevant. That means you can connect with people earlier in their buyer journey. Also, early adopters face less competition and can learn how to optimize for AI queries. Google’s internal data even suggests users find AI-overview ads useful when they’re looking for answers.
Q: Are there downsides or risks to advertising in AI results?
A: There are a few. First, as experts warn, users might feel uneasy if AI chatbots start feeling too much like ad platforms. You must ensure your ad genuinely helps. Second, AI search is new, so metrics and tools are still catching up. For now, you may have to piece together performance data. Finally, the advertising rules differ; for instance, Google won’t show AI-overview ads for sensitive topics. Always keep an eye on policy changes from Google and OpenAI.
Q: How much do AI advertising campaigns cost compared to Google Ads?
A: Exact pricing isn't public yet, but early-stage platforms typically offer lower costs due to less competition. Initial ChatGPT advertising might be cheaper than established Google Ads, though this will change as more advertisers join. Google's AI Overview ads use existing Google Ads pricing models (CPC, CPM) with costs varying by industry and competition.
Q: Will this change SEO or organic search traffic?
A: Potentially. Since AI Overviews often appear at the top, traditional click-through rates may drop unless your site is one of the cited sources. The good news is, if your site is authoritative and content-rich, Google might cite it in the AI summary. That exposure still boosts trust, even if clicks go down. In essence, SEO still matters – just focus more on comprehensive, user-focused content that AI would pick up.
Q: Will AI advertising replace traditional search advertising?
A: No, AI advertising will complement rather than replace traditional search advertising for the foreseeable future. Google still shows traditional text ads alongside AI Overviews, and many searches don't trigger AI responses at all. Different ad formats serve different purposes and reach different user mindsets. Your strategy should include both AI advertising and traditional search ads, plus social advertising, display, and other channels. Multi-channel approaches will remain the most effective way to reach customers across their entire journey.
Q: How do I measure ROI on AI advertising when attribution is complex?
A: Track multiple metrics beyond direct conversions. Monitor citation frequency (how often your brand appears in AI responses), share of voice against competitors, assisted conversions where AI introduces customers who convert later, engagement depth in conversational platforms, brand lift through surveys, and quality of traffic measured by engagement and conversion rates. Use UTM parameters and dedicated landing pages to track AI advertising traffic specifically. Set up view-through conversion tracking to capture delayed conversions. Accept that some AI advertising value will be indirect—brand awareness and consideration that pays off across multiple channels over time.
Q: What content types work best for getting mentioned in AI results?
A:Comprehensive guides addressing topics thoroughly, FAQ pages answering common questions directly, case studies with specific data and results, comparison content evaluating options objectively, how-to guides with step-by-step instructions, expert commentary demonstrating genuine knowledge, and video content explaining concepts clearly. The common thread: content that genuinely helps users make decisions or solve problems performs better than content designed purely for ranking. New Zealand-specific content addressing local business challenges, market conditions, and regional examples resonates particularly well with AI systems serving Kiwi users.